Ideally, I would like to compile a USB installer that will include all versions for Windows 7 in both 64bit and 32bit, and install in both EFI and Legacy BIOS configurations, but I suspect this is not possible. So far I have created an installation USB with all versions of Windows 7 64bit, added some drivers, and removed the ei.cfg file. Hiren’s BootCD PE supports UEFI booting from DVD and USB flash drives. To format, re-partition your USB drive and to copy the ISO content into your USB drive properly, we have developed Hiren’s BootCD PE – ISO2USB portable tool. You need Administrator privileges to run it. It is free both for commercial and non-commercial use. This guide explains how to create a Windows bootable USB drive for the following Windows versions: Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10. Creating a bootable USB drive will allow you to install Windows from the USB drive directly. To be able to install Windows from a USB, you need have one of the following: the ISO image of the Windows version. Can't boot the USB drive when it is NTFS partition. Only FAT32 is bootable in UEFI mode. I created UEFI bootable USB from the 64 bit Windows 7 ISO image I downloaded from msdn. It still freezes on start-up logo. I can boot and proceed to the installation screen if I use Legacy Mode instead of UEFI. Using Windows 7 USB/DVD Download Tool. To create the bootable drive with the Windows 7 USB/DVD Download Tool, follow the steps from Using the Windows 7 USB/DVD Download Tool from Windows 8/8.1. While the name is “Windows 7”, you can use the tool for Windows Vista systems too. If you have the installation disc (DVD).
Up to now I have done xcopy all the files from Windows 7 install DVD to bootable USB flash drive. But when I entered into EFI shell and I selected the removable harddisk device (that is fs0 indicating as USB flash drive). Insert the USB bootable media drive and switch on your computer. If the default setup in your BIOS or UEFI mode is configured accordingly or if you have manually done the same, your will PC will.
1. Introduction:
Microsoft Windows installation is nowadays mostly carried out using USB flash drives. This method is more convenient when compared to the traditional CD/DVD drive method. However, small number of users may still be using the traditional CD/DVD drives for installing windows due to its simplicity. In this article the focus is on preparing external bootable USB drives, which can be external USB flash drive or external USB hard drive. However, the same rule will still apply if you are using a CD/DVD drive with a slight difference.
Modern systems have evolved in the way they boot the operating system and have increased in complexity. For example, Microsoft Windows 10 is mostly installed using bootable USB drive. This guide aims to address failed USB Windows 10 installation and the correct procedure to fix and avoid Windows booting problems.
If Windows 10 won’t boot or you have failed Windows installation then check the booting table below first. To simplify the booting process options, we have developed a unique UEFI/MBR boot table that users can use as a reference guide when they encounter booting issues such as Windows 10 not booting, see section 4 below.
For more advice on how to troubleshoot pc problems see our PC Repair Troubleshooting Tips page, or for full lists of our current PC Blogs see our Blogs Section.
2. How to Install Windows 10/8/8.1/7 From USB Drive:
In this section we will show you how to install Windows 10 from USB drive. This instruction applies to all Microsoft Windows operating systems including:
■ Installing Windows 10 from USB drive.
■ Installing Windows 8.1 from USB drive.
■ Installing Windows 8 from USB drive.
■ Installing Windows 7 from USB drive.
The format of the installation files in the USB drive must comply with the requirements in order to install windows successfully.
However, you can assume that most modern ISO installation files for modern systems or utilities are UEFI compatible. In comparison if you have an old computer then it may not be UEFI compatible therefore you need to adjust your BIOS settings and hard drive format accordingly as described below.
Microsoft Windows setup screen
To install Windows 10/8/8.1/7 in UEFI mode:
This procedure is for installing Windows from ISO file (You can use this step by step procedure for preparing any bootable media, not just Microsoft Windows)
1. Download Windows ISO file, make sure it is UEFI compatible, ie UEFI ready. (Must have the folder (EFIbootbootx64x.efi).
2. Use Rufus utility to create bootable media, select UEFI mode.
3. Set your system bios to UEFI mode.
4. Disable secure boot in the system Bios.
5. Select boot from USB in bootable order under system Bios.
6. Hard drive format must be in GPT type or let the install utility auto format your disk.
7. After installing Microsoft Windows go to system Bios and re-enable secure boot.
To Install Windows in Legacy Mode (Windows 7, Windows 8/8.1 or Windows 10):
This is ideal for older type of computers or windows 7 install in particular.
1. Download ISO file, make sure it is MBR compatible. (Does not contain the EFI folder).
2. Use Rufus utility to create bootable media, select MBR mode.
3. Set your system bios to Legacy mode or CSM mode (Compatibility Support Module).
4. Select boot from USB in bootable order under system Bios.
5. Hard drive format must be in standard MBR type or let the install utility auto format your disk.
EFI boot error messages:
If you encounter EFI boot error messages while booting from USB media or your bootable USB drive is not showing (bootable device not detected), please check the following:
■ Disable secure boot option in the Bios.
■ Disable fast boot option in the Bios, if available.
■ Enable Uefi boot in the Bios options.
■ Format USB media with FAT32 or use Rufus utility.
■ Make sure that USB ISO file is UEFI compatible.
■ Set your Bios option to CSM (last resort).
This will allow installation media to boot successfully and prevent error screens popping up. However, please re-enable the secure boot option after finishing the installation for added protection of your system. Please use our reference booting table below in section 4 for troubleshooting boot errors.
Prepare USB media for bootable installation:
To install Windows from USB media you need to need to use a special utility in order to make the USB drive bootable. The most common utility is provided by Microsoft and known as Windows Installation Media. An alternative option is to use the Rufus utility as it has a very flexible approach. Unlike Microsoft tool, this utility has many options that can be configured to meet your requirements.
Hardware BIOS options also must have the correct settings to enable the system to boot. Usually the BIOS options are accessed by pressing a special function key such as F2 after powering up the system. For example to boot Windows 7 in UEFI mode you must have a supported motherboard with efi mode enabled. The figure below shows a BIOS screen taken from a Dell computer. Modern systems commonly include four options for booting: Legacy MBR, Legacy UEFI (CSM), UEFI only and Secure Boot. Once again, these options must be aligned with the format of the internal hard drive and bootable media type.
You must ensure that your hard drive is formatted as GPT if you have selected UEFI format in the bios option. The format process is done automatically by the windows ISO file and you need not to worry about it.
If you encounter further errors during the installation process please check the boot reference table below in section 4 to resolve your issues.
3. UEFI Boot Mode:
New BIOS standard, known as UEFI, was introduced in 2012. Microsoft Windows 8 was the first version to utilise this new technology, followed by Microsoft Windows 10. In contrast, Microsoft Windows 7 is usually installed using the MBR disk format.
A common question is Uefi vs Legacy, Uefi vs MBR or Uefi vs Bios, What is the difference?
The new method of Uefi booting has introduced new improvements to the traditional legacy MBR based BIOS. Among these improvements are: Improved security, faster booting time, increased number of possible partitions and support for hard drives that are larger than 2TB. Please note that the legacy booting mode also referred to as MBR or traditional Bios.
For a successful UEFI mode booting many conditions must be satisfied:
- 64-bit operating system (with minor exceptions).
- GPT based hard drive partition.
- Additional FAT32 partition for boot files.
In the legacy MBR format, hard drives can have up to 4 primary partitions with NTFS/FAT32 format and boot files are stored inside the system partition, usually C drive. However, in the UEFI mode a FAT32 partition is required for storing the boot files. This is in addition to the standard system drive, which is usually ANTS formatted. Furthermore, for UEFI Bios mode the hard drive must be initialised as GPT format.
Finally, there is a hybrid booting mode known as CSM (Compatibility Support Module) which is available to most modern computer systems Bios. In this booting mode, it is possible to boot a legacy operating system in a modern Uefi setup.
So what is the difference between Uefi and CSM, or Uefi vs CSM you may ask?
The CSM booting mode is one of the most misunderstood concept and people simply mistakenly believe it is another legacy mode. In fact the main purpose of having a CSM booting mode is to allow legacy or Uefi media/system to boot in a UEFI hardware.
For example, if you have a bootable Uefi USB media or Hard drive containing windows 10 operating system then this will boot under either Uefi or CSM modes but not legacy Bios. Similarly, if your USB media or hard drive is legacy based, it will boot under both legacy and CSM Bios options. The section below explains in further details all of these booting modes and how to successfully boot a system.
4. UEFI Boot Reference Table:
In order to simplify the booting process, we have created a UEFI/MBR boot table as shown below. The area in green shows the conditions for a successful booting process, whereas the area shown in red displays a failed booting process. The column (LegacyUefi) is better known as CSM boot mode. If you can match the settings of your hardware (motherboard), bootable USB/CD drive and internal hard drive, only then your system will boot correctly.
The table above assumes the following possible combinations:
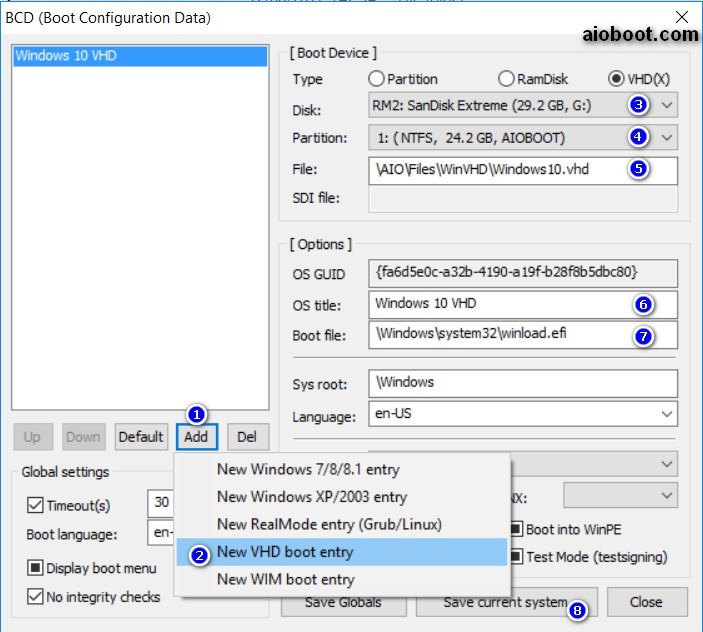
- 2 hard drive formats (MBR, GPT).
- 3 motherboard BIOS settings (legacy bios, legacy uefi, uefi).
- 4 external USB drive settings (iso-uefi-fat32, iso-uefi-ntfs, iso-mbr-fat32, iso-mbr-ntfs).
So in theory there are a possible combinations of events totalling (2 x 3 x 4 = 24). These combinations are not set in stone and it is possible to expand it to include further variations such as; secure boot, NTFS, FAT32, etc. However, it is more practical to reduce the size of the compatibility reference boot table in order to make it more usable and decrease complexity.
The UEFI/MBR reference boot table includes some assumptions that have been made and referenced in the legends under the table. For example, the secure boot option setting may impact the success of the booting process. It is therefore recommended to disable this option during the installation process, and re-enable it after the completion of Windows installation.
If you are using a bootable CD/DVD drive instead of a USB drive then the proposed Reference Boot Table below will still apply. However, you may encounter improved compatibility when booting CD/DVD that contains UEFI files. This means CD/DVD that contains images based on UEFI format may still boot under both legacy or UEFI modes. If the CD only contains the standard MBR files then it will only boot under legacy settings.
5. Summary:
Please observe the following for a successful booting process:
Windows 7 Boot Media Usb
- Use the UEFI/MBR reference boot table to check if your settings are correct.
- MBR scheme should only be used with older systems or 32-bit OS versions.
- New computers should use the UEFI scheme where possible for the advantages mentioned earlier.
- Disable secure boot if you are using modified ISO files or having booting issues. Don’t forget to re-enable this option to secure you system.
- UEFI will only work with 64-bit systems (with minor exceptions).
- UEFI requires GPT based hard drive.
- UEFI stores boot file on a separate FAT32 partition.
- IF your bootable ISO image is UEFI based and contains a file that is larger than 4GB, then you will need two partitions inside your USB drive. First partition must be a FAT32 for storing boot files, and a standard NTFS partition for storing system files. There are utilities available such as Rufus that will automatically partition your USB drive to meet these requirements.
- If you are still using CD/DVD drive the MBR/UEFI reference boot table is still valid. However, depending on your hardware, you may find that it is a little more flexible with UEFI booting. For example, you may be able to boot a UEFI DVD using the legacy mode.
- The proposed boot table is also valid for any bootable software/utility and not just Microsoft Windows software.
Windows 7 Efi Boot Usb 3.1
Finally, if your system is already formatted and you change the BIOS options, your system may not boot successfully. Once again, use the proposed boot table above to check that all the set parameters are compatible. This procedure, if followed, will help you repair any system not just Windows 10, that is not working or not booting properly.